Recent advances in AI and big data analytics have led to a new concept called “smart farming.” This concept, also known as “precision agriculture” or “digital farming,” refers to the use of advanced technologies and data-driven approaches to improve agricultural productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Specifically, it involves integrating modern technologies into traditional farming practices to monitor, automate, and optimize agricultural operations. Table 1 describes the key farming technologies involved and their value to the smartness objective.
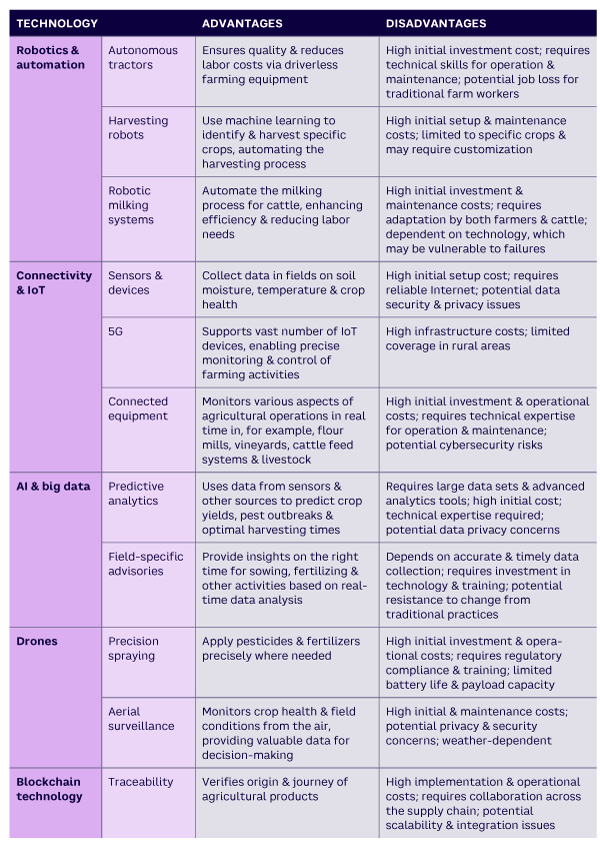
As Table 1 shows, advanced farming methods use technologies like AI, GPS (Global Positioning System), Internet of Things (IoT), satellite imagery, and data analytics to optimize crop management. These technologies improve productivity, resource efficiency, and environmental sustainability by providing precise information for managing inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides. They can also reduce costs, enhance crop yields, and minimize environmental impact, but they require a significant initial investment and strong technical and data management skills.
In essence, big data and AI can integrate the social, environmental, and economic sustainability components of farming. This is crucial for realizing a holistic approach to sustainable agriculture. Social sustainability enhances farming and rural communities by developing shorter supply chains, fostering community involvement, and promoting youth development. Environmental sustainability focuses on mitigating carbon footprints, minimizing food waste, and enhancing food quality and security, primarily through lifecycle assessments and resource-recovery practices. Economic sustainability aims to reduce overall supply chain costs, boost productivity, and ensure long-term profitability by adopting strategies like short supply chains and the promotion of local food products.
Together, these sustainability components can lead to robust, resilient agriculture that not only supports economic growth but also protects the environment and enhances social well-being.
[For more from the author on this topic, see: “From Labor-Intensive to Smart Farming: Impact of Big Data Analytics & AI on Hydroponics.”]