This Advisor focuses on Lusatia, a German region historically reliant on lignite (brown coal) for energy, and its ongoing transformation under Germany’s ambitious Energiewende policy, which aims for climate neutrality by 2045. The transition involves closing all coal plants by 2038 and shifting to renewable energy. The region’s transformation is guided by the Act to Reduce and End Coal-Fired Power Generation and the Structural Development Act, which provide financial and legal frameworks to support affected regions, including Lusatia.
The German government allocated €40 billion (US $43 billion) to support the transition, which includes infrastructure projects and job creation. The Energy Innovation Center (EIZ) at Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg (BTU) is central to Lusatia’s transformation, supporting innovation and technology development.
EIZ: Engine of Structural Change in Lusatia
EIZ was established in 2022 to drive the regional energy transition through research, entrepreneurship, technology transfer, and collaboration with industrial partners and other research institutes in the region. It is cofinanced with up to €102 million (US $112 million) for up to 10 years by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) in partnership with the Investment Bank of the State of Brandenburg.
EIZ’s Approach to Research & Innovation
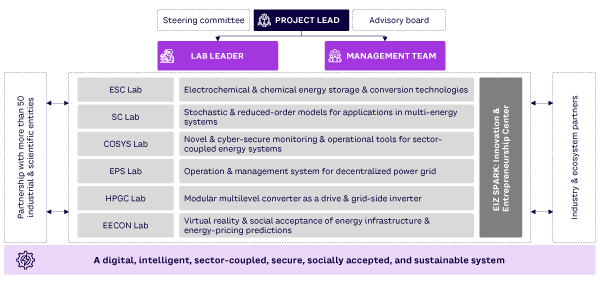
The center comprises six interconnected and interdisciplinary research labs, each with a thematic focus (see Figure 1). With 15 professors, ~70 researchers and technicians at BTU, six project and innovation managers, and more than 50 additional partners from business and science, EIZ is ideally positioned for interdisciplinary research.

All EIZ research activities are dedicated to developing renewable energy technologies to replace Lusatia’s lignite-based power production system. In a complementary approach, involved labs are developing novel solutions for establishing digital, intelligent, sector-coupled, secure, socially accepted, and sustainable energy systems in collaboration with ecosystem partners in the region and beyond (see Figure 2).
EIZ is dedicated to product-oriented technology development and bridging the gap between research and industry application through open innovation concepts. To enhance this approach, EIZ SPARK was formed in 2023 to act as an innovation and entrepreneurship center, where energy researchers and students drive the transition to a sustainable energy system by creating an open innovation ecosystem that accelerates knowledge and technology transfer from the labs to the marketplace.
EIZ SPARK comprises entrepreneurs in residence and experts in energy technology, entrepreneurship, and innovation management to leverage both practical and conceptual expertise to achieve this mission. Unlike technology transfer centers that operate as independent entities across economic sectors, EIZ SPARK is closely integrated with EIZ research groups. This ensures ongoing interaction with researchers and emphasizes entrepreneurship and technology transfer.
EIZ’s generous funding for basic research and infrastructure enabled the purchase of necessary lab equipment and the hiring of approximately 70 researchers. The project also gained considerable political backing, with high-profile visits from the German president, ministers, state secretaries, and international ambassadors that elevated the project’s visibility.
The project quickly achieved significant academic success. Researchers presented their work at more than 40 global conferences and published more than 30 peer-reviewed articles within the first two years. The group participated in over 100 events, industrial fairs, and exhibitions, building partnerships with governmental and industrial organizations.
[For more from the authors on this topic, see: “Germany’s Energy Innovation Hub: A Catalyst for Climate Neutrality.“]